When managing your website’s SEO, you may come across the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag status in Google Search Console (GSC).
While this notice might initially seem alarming, it’s typically informative rather than indicative of a critical issue.
In this article, we’ll explain what this status means, why it occurs, and how you can address or manage it effectively.
In This Article
- What Does the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Status Mean?
- How to Find the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Status in Google Search Console
- How to Find the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Status using Index Status in All in One SEO’s Search Statistics Feature
- How to Manage This Status
What Does the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Status Mean?
The Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag status indicates that Google has identified multiple versions of a page on your website. These versions share the same canonical URL—the original or preferred version of the page.
Canonical tags guide search engines to prioritize one version of a page when duplicates exist. By marking alternate URLs, Google ensures that its index remains clean and focused, reducing the risk of duplicate content issues.
This is a common scenario in WordPress sites where URLs with query parameters or session IDs lead to the same content. For example:
- Canonical URL: https://example.com/demo
- Alternate URL: https://example.com/demo?filter=1
Google marks the alternate version but indexes the canonical one, ensuring the correct URL appears in search results.
Why Does This Status Occur?
This status typically arises due to the following:
- Query Parameters: URLs with additional parameters that modify the content presentation, such as filters or tracking IDs.
- Session IDs or Tracking Tags: URLs appended with unique identifiers for user sessions or marketing campaigns.
- Duplicate Content Handling: Pages with identical content, but you only want to index one and set the same canonical URL for both.
Google’s goal is to avoid indexing duplicate URLs and focus on the canonical version to streamline indexing and ranking processes. This ensures users and search engines are directed to the most relevant version of a page.
Does This Require a Fix?
In most cases, no action is necessary. The Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag status is simply informational, confirming that Google has identified and resolved potential duplication. However, consider making changes if:
- You no longer need the alternate URL.
- Alternate URLs cause confusion or unnecessary complexity.
- The alternate URL negatively impacts analytics or user experience.
How to Find the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Status in Google Search Console
To identify pages with the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag status in Google Search Console (GSC), follow these steps:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account and select the appropriate property (website) in the Search property drop-down (if you manage multiple websites).
- Click on Pages under Indexing in the left-hand sidebar.

- In the Page indexing report, scroll down to the Why pages aren’t indexed section and look for Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag. Click on this to see a detailed list of all pages flagged for this reason.
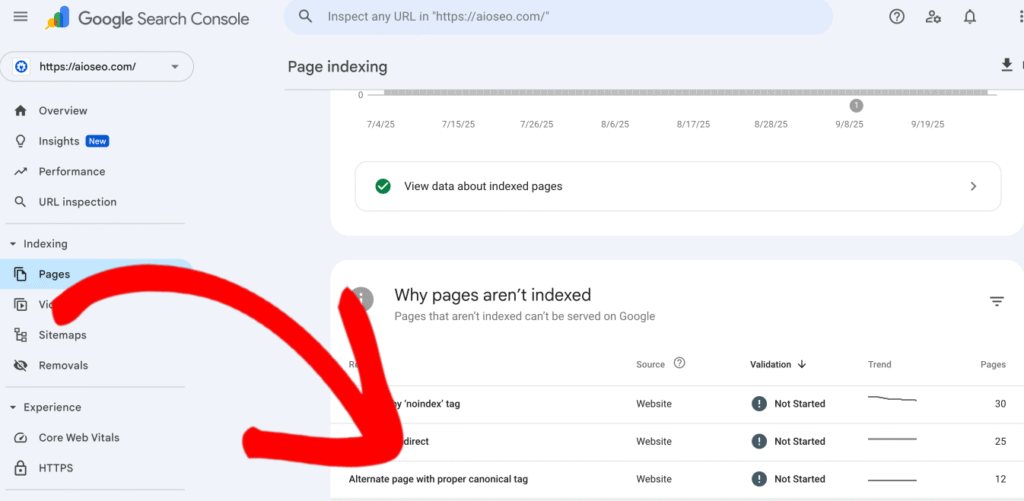
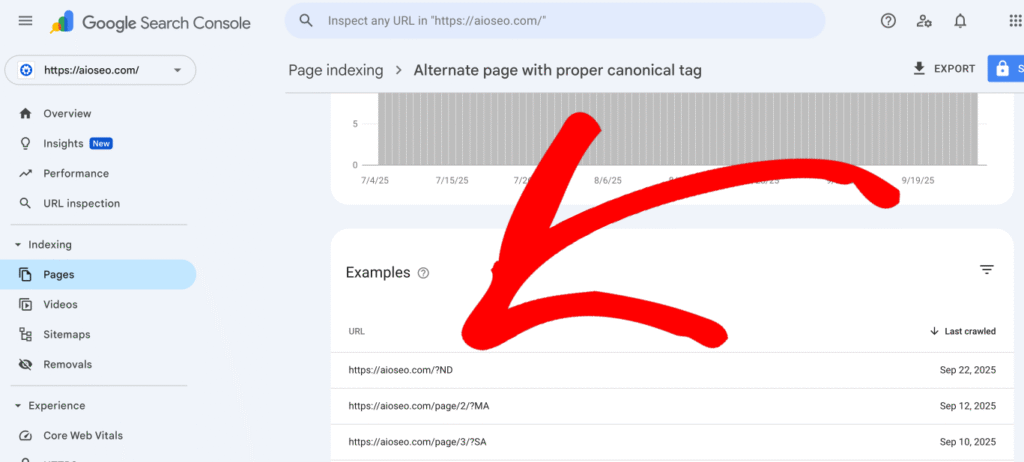
- After you click on the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag, scroll down to the Examples section to view the list of affected URLs. This will help you understand whether the redirect is intentional or if there are issues, like broken links or incorrect redirect types.
How to Find the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Status using Index Status in All in One SEO’s Search Statistics Feature
IMPORTANT:
Before getting started, make sure to connect Search Statistics to your Google Search Console account. You can find instructions on how to connect to your Google Search Console account here.
NOTE:
The Index Status feature is available to customers with an Elite plan for All in One SEO Pro. Upgrade to All in One SEO Pro today to get Search Statistics and many more features!
The Index Status feature enables you to see Google Search Console errors directly within your WordPress dashboard. To do this, follow these steps:
- Click on Search Statistics in the All in One SEO menu and then click on the SEO Statistics tab.

- In the Content Performance report, you’ll find a column labeled Indexed, which shows the index status of your pages using color-coded icons.

- If any of these icons are orange or red, hover over them to reveal a detailed popup. If the issue is an Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag status, then the popup will provide specific information.


- Alternatively, navigate to the All Posts or All Pages screen in WordPress. The AIOSEO Details column on this page displays the same index status icons as the Content Performance report. Hovering over an icon here will also show details of any errors.

By using these methods in All in One SEO, you can effectively locate and address URLs affected by the Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag status, ensuring a smooth user experience and optimal indexing for your site. You can learn more about Checking the Index Status of Content in our article here.
How to Manage This Status
- Ensure You’ve Set The Correct Canonical URL:
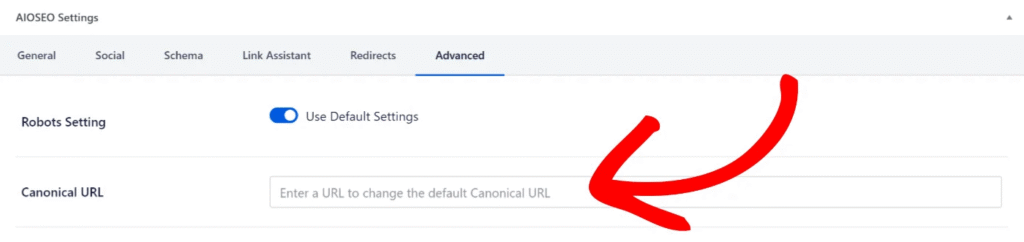
Edit the affected page in WordPress. Scroll down to the AIOSEO Settings section and click on the Advanced tab. Enter the preferred URL in an absolute format, such as https://yourdomain.com/preferred-page in the Canonical URL field, and save your changes. This ensures that search engines recognize the URL you prefer for indexing.
You can learn more about changing canonical URL in our article here.
- Add a 301 Redirect with AIOSEO:
AIOSEO provides robust options to handle redirection, including the ability to redirect query parameters. If you’re seeing unwanted query parameters being reported, you can create tailored redirects to handle these efficiently.
When setting up a redirect, follow these steps to specify how query parameters should be handled:
- Open your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Redirects in All in One SEO menu.
- In the Source URL field, enter the alternate URL (the one you want to redirect from). For example:
https://example.com/demo?filter=1 - In the Target URL field, enter the canonical URL (the one you want to redirect to). For example:
https://example.com/demo - Click on the Advanced Settings link next to the Redirect Type dropdown to reveal query parameter options.
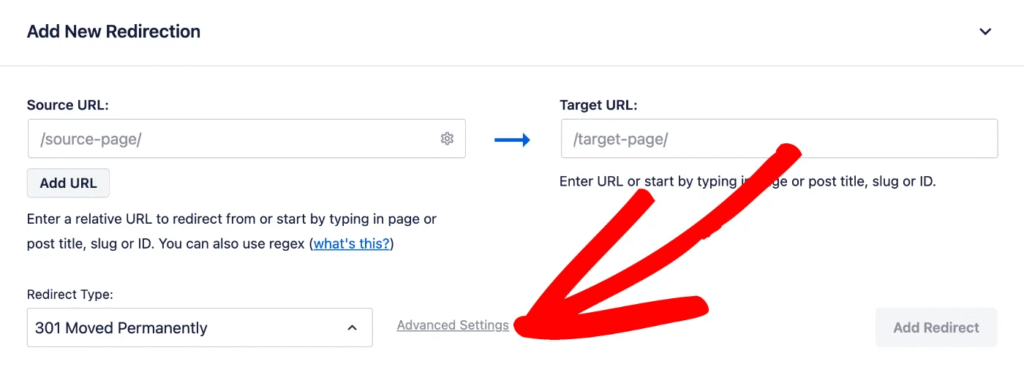
- Select 301 (Move Permanently) from the Redirect Type dropdown menu.
- In the Query Parameters dropdown, select one of the following options:
- Ignore all parameters: Redirects to the target URL regardless of the query parameters.
- Exact match all parameters in any order: Redirects only if all specified parameters match, irrespective of their order.
- Ignore & pass parameters to the target: Passes the query parameters to the target URL while redirecting.
- Ignore all parameters except UTM: Ignore all parameters except UTM tags.
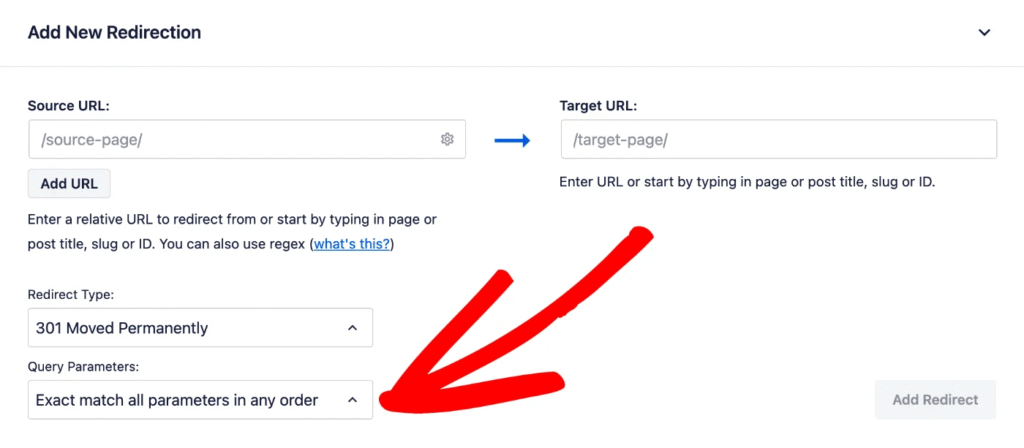
- Click Add Redirect to save your settings.
NOTE:
The Redirection Manager feature is available to customers with a Pro plan or above for All in One SEO Pro.
Upgrade to All in One SEO Pro today to get Redirection Manager and many more features!
NOTE:
AIOSEO also supports bulk redirects. You can upload a CSV file containing multiple source and target URLs to manage redirects efficiently. This feature is especially helpful if you have numerous URLs to redirect. For more details, refer to our article how to redirect URLs in bulk via CSV file.
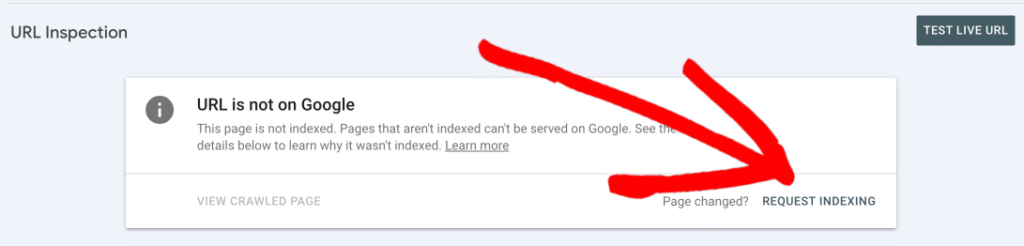
- Submit the Correct URL in Google Search Console:
After making changes in AIOSEO, return to Google Search Console and use the URL Inspection tool to test the affected URL. Click REQUEST INDEXING to prompt Google to re-crawl the page with the updated canonical URL.
Best Practices to Prevent Future Issues
- Consistent URL Structures: Avoid unnecessary query parameters or duplicates by standardizing URL formats across your site.
- Canonical Tags: Ensure proper canonical tags are set for all pages to guide search engines effectively.
- XML Sitemaps: Use AIOSEO’s Sitemap feature to include only canonical URLs in your sitemap. This prevents unnecessary alternate URLs from being indexed.
- Regular Audits: Periodically review your site’s indexing status using Google Search Console and tools like AIOSEO’s Search Statistics to catch potential issues early.
- Avoid Duplicate Content: Consolidate similar pages and use canonical tags or redirects as needed to reduce redundancy.
The Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag status is typically a non-issue and a confirmation of Google’s effective handling of duplicate URLs.
By reviewing affected URLs, setting up redirects if necessary, and following best practices, you can ensure that your site is optimized for search engines and users alike.
AIOSEO’s tools simplify managing redirects and canonical tags, ensuring a smooth user experience and better search engine performance.