The Duplicate without user-selected canonical status in Google Search Console indicates that Google has found multiple pages with similar content but cannot determine the main page to index. This can lead to lower search rankings as Google splits ranking signals between duplicate pages.
While this issue may seem complex, resolving it is straightforward with All in One SEO (AIOSEO).
In this guide, we’ll explore what this status means, why it occurs, and how to fix it effectively.
In This Article
- What Does Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical Mean?
- How to Find the Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical Status in Google Search Console
- How to Find the Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical Status using Index Status in All in One SEO’s Search Statistics Feature
- Fixing Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical with AIOSEO
What Does Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical Mean?
This status occurs when Google discovers duplicate pages but no canonical tag is present to specify the main version. Here’s why this might happen:
- URL Variations: Pages with different query parameters or accessible through www and non-www versions.
- Missing Canonical Tags: No rel=”canonical” tag is defined for the duplicate pages. The absence of a canonical URL leaves Google guessing the primary page.
- Duplicate Metadata: Identical meta titles, descriptions, and content make it difficult for search engines to distinguish between pages.
By addressing these issues, you can ensure Google indexes the intended pages, improving your SEO performance.
How to Find the Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical Status in Google Search Console
To identify pages with the Duplicate without user-selected canonical status in Google Search Console (GSC), follow these steps:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account and select the appropriate property (website) in the Search property drop-down (if you manage multiple websites).
- Click on Pages under Indexing in the left-hand sidebar.

- In the Page indexing report, scroll down to the Why pages aren’t indexed section and look for Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical. Click on this to see a detailed list of all pages flagged for this reason.
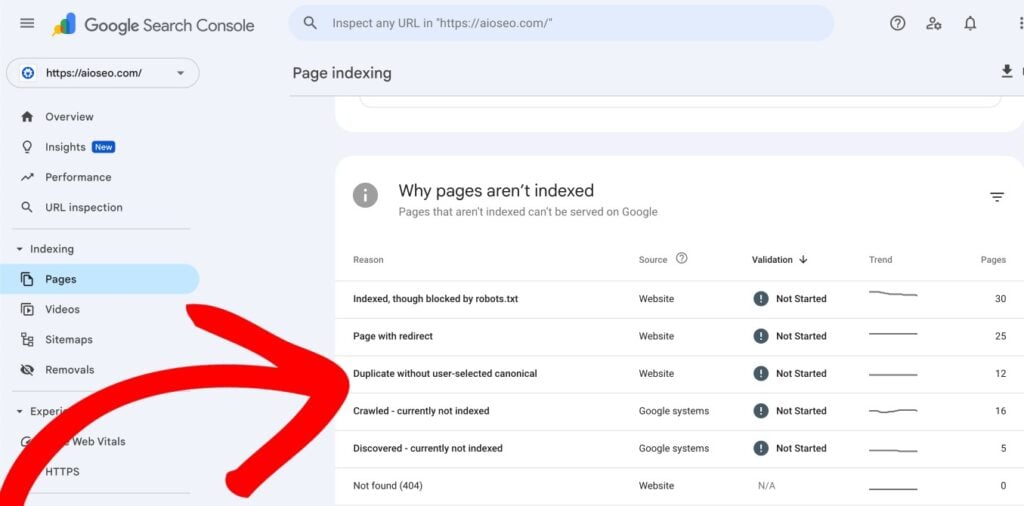
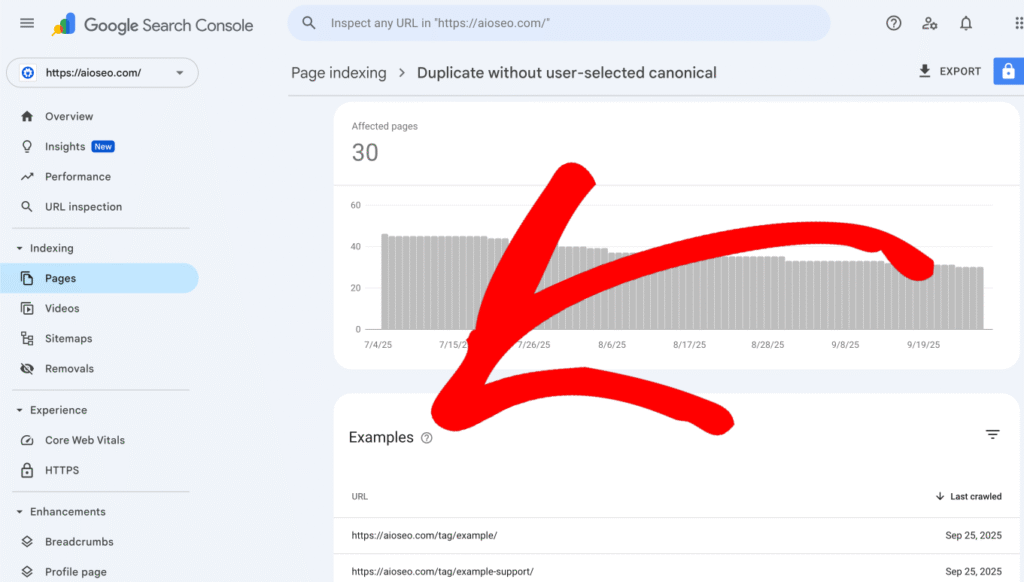
- After you click on Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical, scroll down to the Examples section to view the list of affected URLs. This will help you understand whether the redirect is intentional or if there are issues, like broken links or incorrect redirect types.
How to Find the Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical Status using Index Status in All in One SEO’s Search Statistics Feature
IMPORTANT:
Before getting started, make sure to connect Search Statistics to your Google Search Console account. You can find instructions on how to connect to your Google Search Console account here.
NOTE:
The Index Status feature is available to customers with an Elite plan for All in One SEO Pro. Upgrade to All in One SEO Pro today to get Search Statistics and many more features!
The Index Status feature enables you to see Google Search Console errors directly within your WordPress dashboard. To do this, follow these steps:
- Click on Search Statistics in the All in One SEO menu and then click on the SEO Statistics tab.

- In the Content Performance report, you’ll find a column labeled Indexed, which shows the index status of your pages using color-coded icons.

- If any of these icons are orange or red, hover over them to reveal a detailed popup. If the issue is a Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical status, then the popup will provide specific information, such as details about the redirect.


- Alternatively, navigate to the All Posts or All Pages screen in WordPress. The AIOSEO Details column on this page displays the same index status icons as the Content Performance report. Hovering over an icon here will also show details of any errors.

By using these methods in All in One SEO, you can effectively locate and address URLs affected by the Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical status, ensuring a smooth user experience and optimal indexing for your site. You can learn more about Checking the Index Status of Content in our article here.
Fixing Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical with AIOSEO
- Specify a Canonical URL
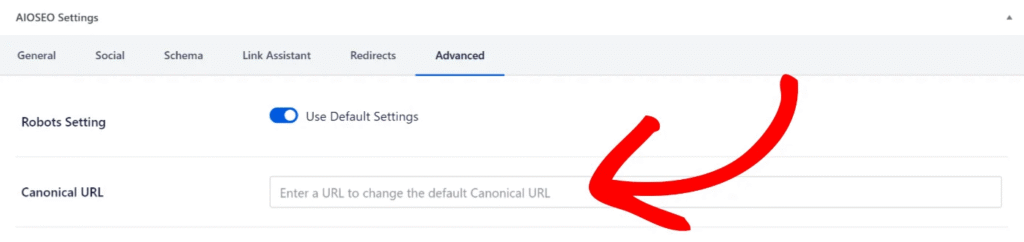
- Start by clearly defining the canonical URL for each duplicate page. Open the affected page in WordPress and scroll down to the AIOSEO Settings section.
- Under the Advanced tab, you’ll find the Canonical URL field.
- Enter the preferred URL in an absolute format, such as https://example.com/preferred-page. This tells Google that this URL is the primary version of the page.
- Save or update the page to apply the changes. Specifying canonical URLs helps consolidate ranking signals and guides search engines to the correct version.
You can learn more about How to Set or modify Canonical URLs in AIOSEO here.
- Redirect Duplicate URLs
If duplicate pages are already live and indexed, you can use redirects to direct traffic to the correct version. This ensures that visitors and search engines are automatically guided to the correct page, and ranking signals from duplicate pages are consolidated.
Redirects are particularly useful for resolving issues caused by legacy URLs or parameterized content. Follow these steps to set this up in AIOSEO:
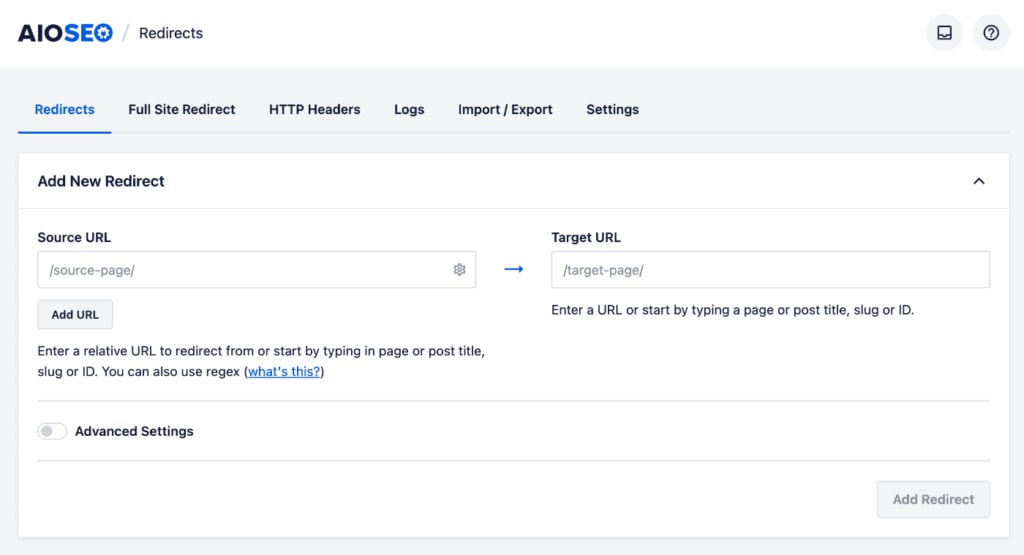
- Navigate to the Redirection Manager in the All in One SEO menu in your WordPress dashboard.
- Enter the duplicate URL as the Source URL.This is the URL you want to redirect from.
- Enter the canonical URL in the Target URL field. This is the URL you want to redirect to.
- Select the redirect type as 301 (Moved Permanently) from the dropdown menu.
- Click the Add Redirect button to save the redirection.
NOTE:
The Redirection Manager feature is available to customers with a Pro plan or above for All in One SEO Pro.
Upgrade to All in One SEO Pro today to get Redirection Manager and many more features!
NOTE:
AIOSEO also supports bulk redirects. You can upload a CSV file containing multiple source and target URLs to manage redirects efficiently. This feature is especially helpful if you have numerous URLs to redirect. For more details, refer to our article how to redirect URLs in bulk via CSV file.
- Use NOINDEX Robots Meta Tag
Instead of blocking duplicate pages in robots.txt, use the NOINDEX tag to prevent them from appearing in search results while still allowing Google to crawl them.
- Edit the duplicate page or post in WordPress and navigate to the Advanced tab in the AIOSEO Settings section.
- You'll see a setting for Robots Settings with a toggle that's set to Use Default Settings.

- Change the toggle to off and you'll see some checkboxes under the Robots Meta heading.

- Check the No Index box and click the Update button for your post. This informs search engines to skip indexing the page without hindering their understanding of your site’s structure.
- Optimize Your Sitemap
A clean sitemap ensures search engines focus on your site’s important pages.
- Navigate to the Sitemaps section in the All in One SEO menu in your WordPress dashboard.
- Click Open Sitemap to review the URLs included in your XML sitemap.
- If duplicate URLs are present, you can easily exclude URLs from your sitemap by scrolling down to the Advanced Settings section in the Sitemap settings.

- Click the toggle to display the Advanced Settings.

- Here you’ll see settings for Exclude Posts / Pages and Exclude Terms.
- In the Exclude Posts / Pages field, start typing the title of any post, page or other post type in this field and a drop down will appear that shows matching content.
- Click on the content you want to exclude and it will be added in the field.

- You can then repeat this by typing the title of any content and selecting it.
This ensures that only canonical URLs are included in the sitemap submitted to Google. Once updated, search engines will focus on the correct pages.
IMPORTANT:
This step doesn't alone stop search engines from finding this content on their own. If you want to stop them from finding and indexing content then you’ll need to ensure a noindex robots meta tag to prevent search engines from indexing your content.Ensuring noindex tag automatically removes the URLs from the XML sitemap.
- Revalidate in Google Search Console
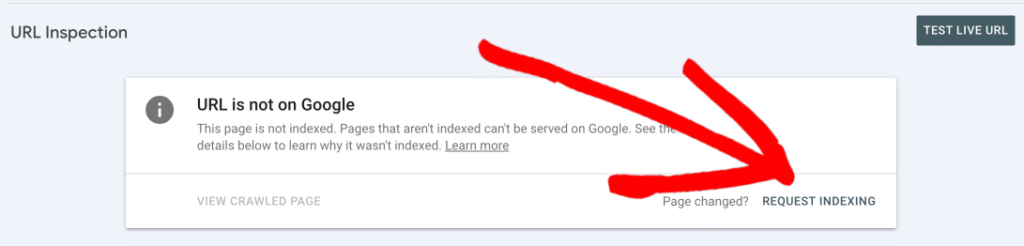
After applying these fixes, log in to your Google Search Console and use the URL Inspection Tool to test the affected URL.
Click Request Indexing to notify Google of the changes. This step prompts Google to re-crawl the page and update its status accordingly.
Preventing This Issue in the Future
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and lead to canonical errors. Use a tool like Siteliner or Ahref’s site audit to scan your website for duplicate or similar pages. Consolidate these pages by merging their content or specifying clear canonical tags for each.
Additionally, maintain consistent URL structures by avoiding unnecessary URL variations (www or non-www) and utilizing HTTPS throughout your site.The Duplicate without user-selected canonical error is common but manageable. By defining canonical URLs, managing redirects, and optimizing your sitemap with AIOSEO, you can ensure that Google indexes the correct pages and improves your site’s SEO.