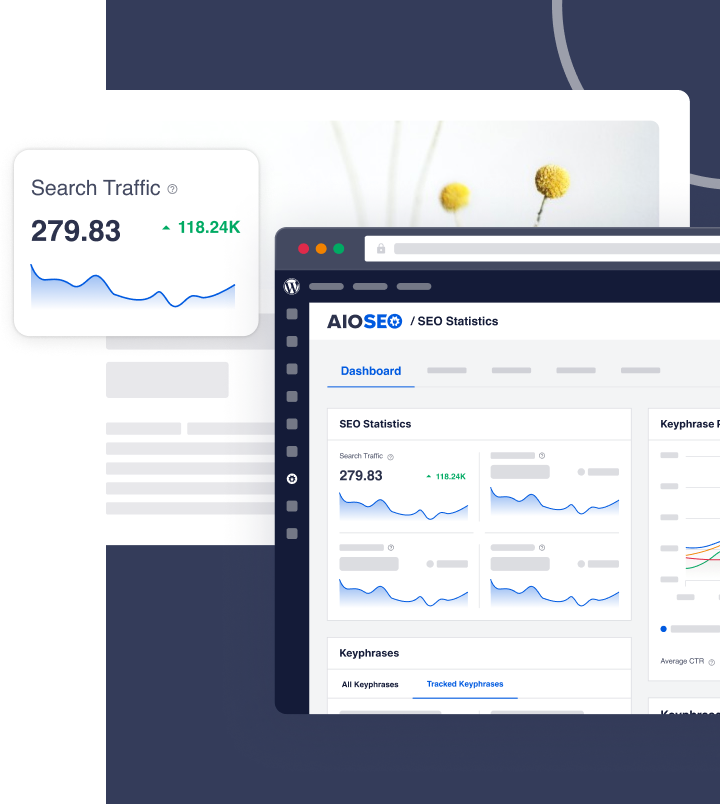
What is indexing in SEO?
Thousands of other small business owners and marketers ask that question daily. That’s because all your SEO efforts hinge on search engines like Google indexing your content.
In this article, we’ll explain indexing in SEO and show you how to optimize your site for better indexing.
In This Article
Before We Get to Indexing, What is Crawling?
Before we answer our main question of the day—what indexing is in SEO— we first need to look at what is crawling.
Crawling is the process search engine bots (also known as search spiders or crawlers) use to systematically browse the internet to discover and access web pages. These bots start from a list of known web addresses (URLs) and then follow links from one page to another, effectively creating a vast interconnected network of web pages.
As the search bots crawl your site, they access your posts and pages, read the content, and follow the internal and external links on those pages. They continue this process recursively, navigating from one link to another until they have crawled a substantial portion of your site.
For small websites, this can be done on all the URLs. However, search bots will only crawl the pages for large sites if they don’t exhaust the crawl budget.
Search engines use the data collected during crawling to understand the structure of websites, the content they contain, and how different web pages are related to each other. The information obtained from crawling is then used for the next step: indexing.
What is Indexing in SEO?
Once the crawlers have found and fetched your web pages, the next step is indexing. This involves analyzing and storing the information collected during the crawling process. The data is organized and added to Google’s index (or any other search engine). This massive database contains information about all the web pages the search engine has discovered.
Search engines use complex algorithms to evaluate and categorize the content found on each page during indexing. For this, search engines consider factors like keywords, page structure, meta tags, and overall relevance during this process.
Why is Indexing Important?
Indexing in SEO is important because it enables search engines to retrieve relevant results when users perform a search query quickly. These indexed results are then displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs).
It’s important to note that not all web pages get indexed, and search engines prioritize pages based on their perceived importance, authority, and relevance. Web pages inaccessible due to technical issues or deemed low-quality should not be indexed.
Should All Your Webpages Be Indexed?
While the default is that all web pages should be indexed, this is not always the case. There may be some instances where you may want to avoid certain pages from being indexed. Examples of such instances include:
Thin Content
If you have pages with minimal or low-quality content that doesn’t provide significant value to users, indexing that content will harm your SEO more than good. These thin pages may hinder search engines from indexing pages that might not contribute meaningfully to search results.
Duplicate Content
Another reason to refrain from indexing some pages on your site is when you have pages with duplicate or substantially similar content. These can lead to potential issues with search engines, particularly penalties or filtering out duplicate content. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version if applicable.
Privacy or Legal Pages
Pages like privacy policies, terms of service, or legal disclaimers shouldn’t be indexed. While these pages are important for legal compliance, they don’t contribute to your SEO strategy.
Temporary or Event-Specific Pages
Seasonal pages or pages related to specific events are another example of pages that don’t have to be indexed. If the content is time-sensitive and not relevant after a certain period, preventing indexing can avoid outdated content in search results.
URL Parameters
URL parameters (also known as query args or query strings) are extra information appended to the end of a URL. They are usually used to pass data to a web page, indicating specific actions or settings to be applied. Because these are dynamically generated pages, they shouldn’t be crawled and indexed.
The decision to not index a webpage should be based on evaluating its value to users and your overall SEO strategy. You can use tools like the “noindex” meta tag or directives in your robots.txt file to guide search engines appropriately.
How Does Indexing Work?
The primary goal of indexing is to create an efficient and searchable catalog of web pages. This makes retrieving relevant results easier for search engines when users perform a search query. Here’s a simplified view of how indexing works:
Crawling
Before indexing, search engines send out bots known as crawlers or spiders to explore the vast expanse of the internet. This involves 2 distinct processes:
Discovery of New Pages
As crawlers navigate the web, they encounter new pages, either through internal links within a site or external links from other sites. When a crawler reaches a page, it downloads all its content, including text, images, and other media.
Parsing and Processing
The content of the discovered pages is then parsed and processed to extract relevant information. This process involves understanding the page’s structure, identifying key elements, and indexing the content appropriately.
Adding to the Index
The information collected during crawling is stored in a massive database known as an index. This index is like a giant library catalog, associating keywords, phrases, entities, and other content-related data with the web pages.
Data Organization
The index organizes the data to make it easy for the search engine to retrieve relevant information quickly. This involves creating an index for various elements associated with each web page, such as words, phrases, and links.
Ranking Indexed Content
Search engines use complex algorithms to analyze the indexed data and determine the relevance and importance of each page. Numerous ranking factors, such as keyword relevance, content quality, and user experience, contribute to how pages are ranked in search engine results.
Query Processing
When a user enters a search query, the search engine looks into its index to find pages that match the query. The algorithm considers various factors to rank these pages based on their perceived relevance to the user’s search intent.
Display of Search Results
Finally, the search engine displays the results on the SERPs. The pages are listed in order of relevance, with the most relevant pages appearing at the top.
The index is continually updated as new content is discovered and changes are made to existing pages. This ensures that search engine results remain fresh and reflect the latest information available on the web.
That’s why you need a tool like AIOSEO’s IndexNow module to help ensure your new or updated content is immediately indexed by platforms that support the IndexNow protocol.
In summary, indexing is a crucial step in the functioning of search engines. It involves systematically organizing web page data to create an easily searchable index, allowing search engines to provide users with relevant and up-to-date results for their queries.
Understanding how indexing works is essential to optimizing your content for improved discoverability and search rankings.
4 Tips for Improving Your Website Indexing
Now that you know what indexing in SEO is, let’s briefly look at a few ways to ensure your posts and pages are indexed quickly.
1. Use the Right WordPress SEO Tool
One of the first steps to ensuring effective indexing is to use the right SEO tool. And for WordPress users, there’s no better tool than All In One SEO (AIOSEO).
AIOSEO is the best WordPress SEO plugin on the market. Over 3 million savvy website owners and marketers trust it to help them dominate the SERPs (search engine results pages) and drive relevant site traffic. The plugin has many powerful SEO features and modules designed to help you optimize your site for greater search visibility.
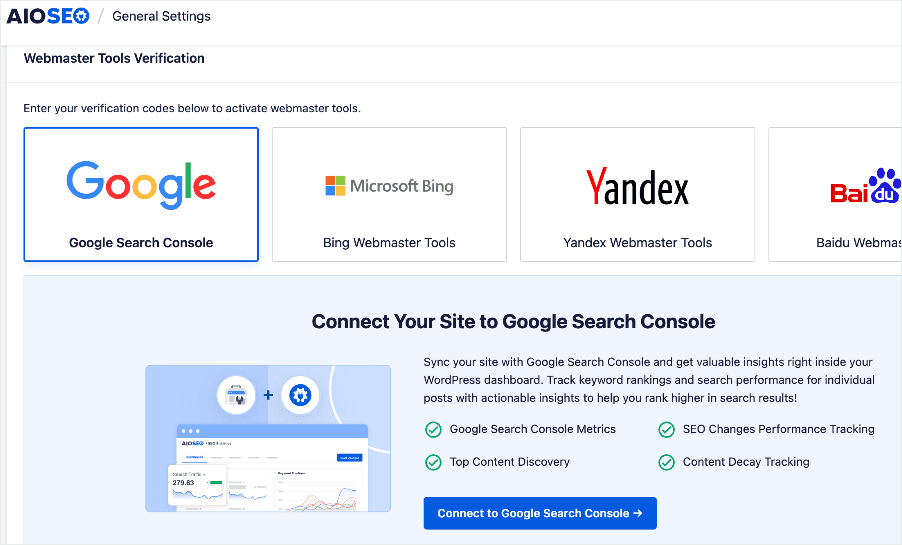
Regarding indexing, one of the most loved is the Webmaster Tools section.

The Webmaster Tools feature lets you connect your site to various platforms, including Google Search Console (GSC). Regarding the lartter, you don’t have to go through the tedious process of copying and pasting verification codes. Connecting your site to GSC helps you submit your sitemaps and content to the search engine for indexing.
Click on the Connect to Google Search Console button to start the connection wizard. The first step requires you to select the Google account you want to use to connect to GSC.
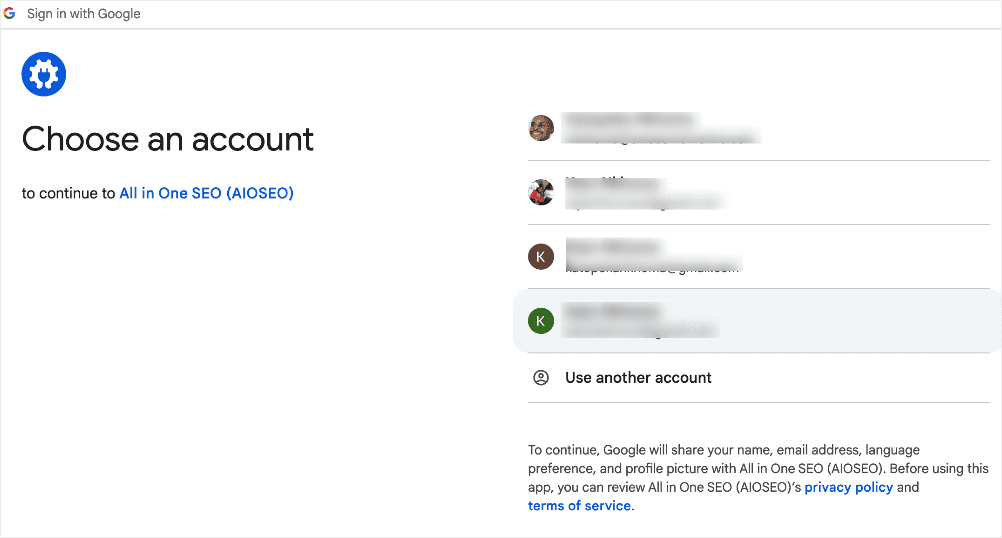
For detailed instructions on using this feature, check out our tutorial on connecting your site to Google Search Console.
For step-by-step instructions on how to install AIOSEO, check our detailed installation guide.
AIOSEO also has many other features to help you boost your local SEO, on-page SEO, and technical SEO. Plus, if you’re a WooCommerce user, AIOSEO has a tailor-made WooCommerce SEO module to help you rank your online store higher in search rankings.
Checking Your Indexing Status in WordPress
AIOSEO also lets you see your index status right from your WordPress dashboard!
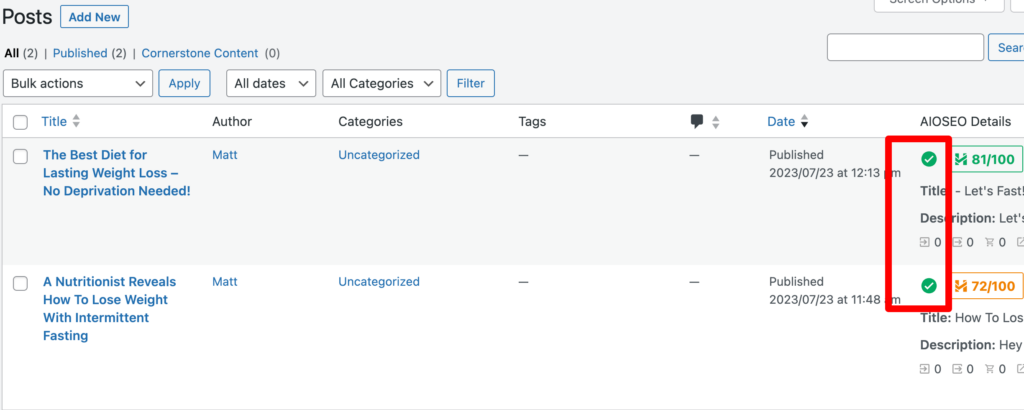
It also gives you other vital information about your URL:
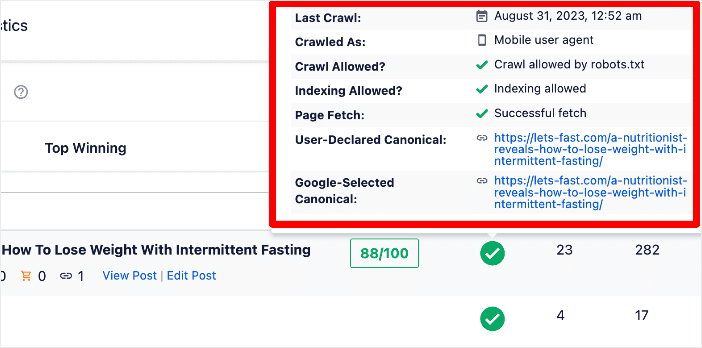
All this helps ensure you know which pages are indexed so you can better troubleshoot those that haven’t been indexed.
You can also check out our list of other Google Index Checker tools you can use.
2. Optimize Your Sitemaps
If you want search engines and users to find your posts and pages easily, you must create an optimized XML sitemap.
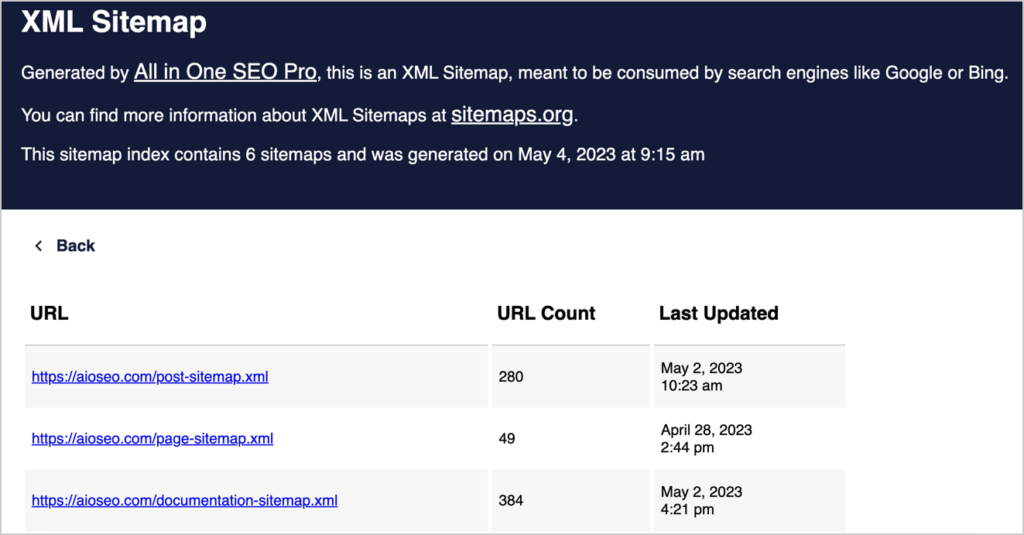
These help search engines crawl and understand your URLs better, resulting in better indexing. Don’t worry if you have lots of pages on your site. AIOSEO makes it easy to add multiple URLs to your sitemap.
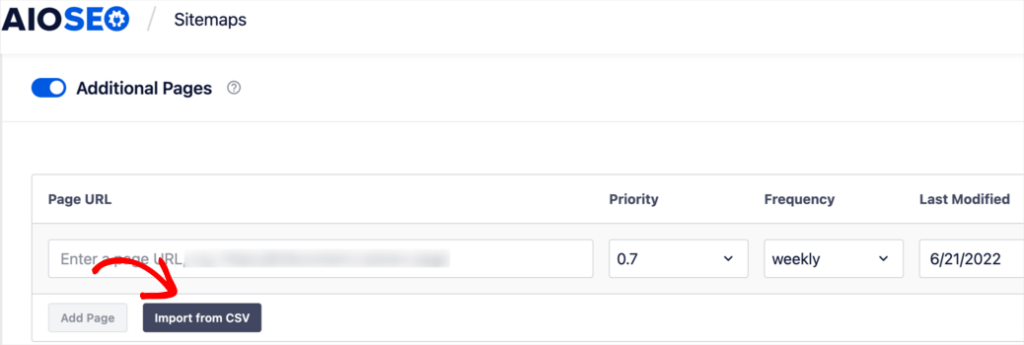
When you submit your sitemap to Google Search Console (GSC), you can easily monitor your URLs for performance and identify potential issues impacting your SEO.
For more details, we’ve created a handy guide to help you create sitemaps in WordPress.
3. Leverage the IndexNow Protocol
The IndexNow protocol makes the internet more efficient by instantly alerting participating search engines of any changes you make on your website.

For example, if you change your content or add a new post or page, the IndexNow protocol will ping search engines about those changes.
Doing so will result in the search engines crawling and indexing your changes faster.
This means IndexNow is a powerful tool to help you get your content indexed faster, resulting in better chances of ranking.
Another significant advantage of IndexNow is that if one search engine participating in the IndexNow initiative is pinged, all other search engines will be alerted when new content is published. As a result, your content will quickly appear in search results for relevant searches.
The best part is that adding IndexNow to your site is easy.
4. Optimize Your Robots.txt File
A robots.txt file is a powerful SEO tool that guides search engine crawl bots or robots on which pages to crawl. As you may have guessed, it’s important that your robots.txt gives Google permission to crawl most of your site.
On the other hand, it’s common to disallow wp-admin pages and other pages irrelevant to your SEO strategy. That’s because they aren’t useful to your search strategy. Telling Google not to crawl unnecessary pages can help boost rankings in search engines and increase page speed.
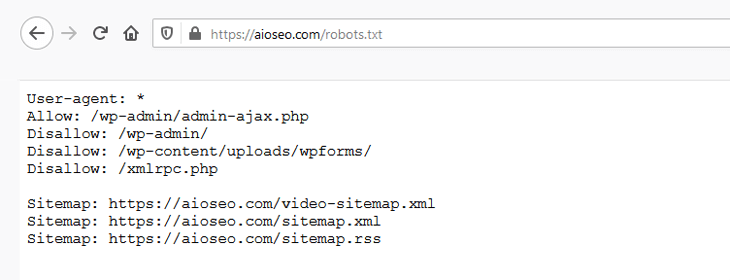
But when it comes to indexing in SEO, you should ensure your important pages are crawlable. You can tell Google bots to allow crawling and even prioritize these URLs. This is super easy to do with AIOSEO’s Robots.txt Editor.
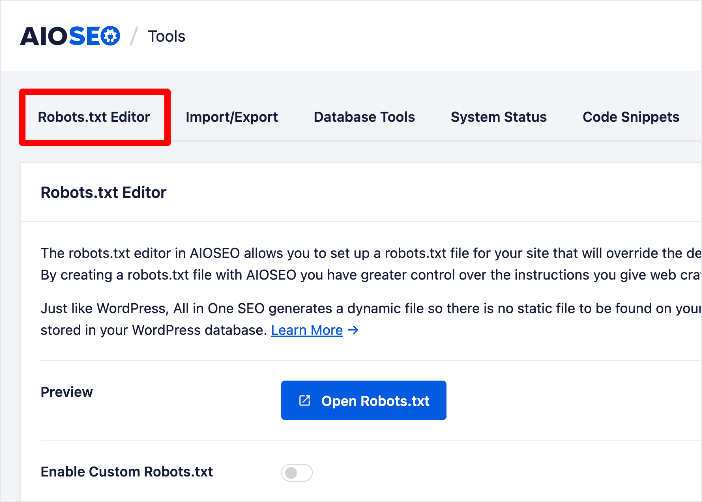
This powerful tool makes optimizing your robots.txt file easy as it comes with many useful directives such as Allow, Disallow, Clean-param, and Crawl-delay.
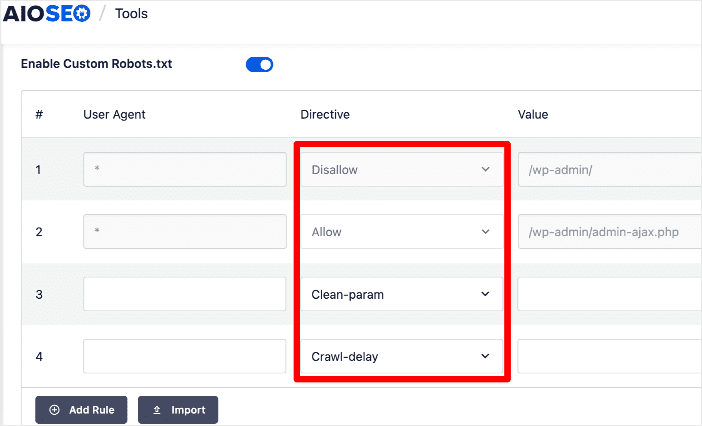
You also have the option to import a robots.txt file from another site, saving you a lot of time optimizing yours.
For more details, please visit our post on how to edit a robots.txt file in WordPress.
Enhancing your site’s indexing is super important to ensuring your content ranks and driving relevant traffic to your site.
For more tips, check out our article on easy ways to index your site on Google.
What is Indexing? Your FAQs Answered
What does “indexing” mean in SEO?
In SEO, indexing refers to the process in which search engines organize and store information gathered during the crawling phase. It involves creating an efficient catalog of web pages, making it easier for search engines to retrieve relevant results when users perform a search query.
Why is indexing in SEO important?
SEO indexing is crucial for visibility in search engine results. Well-indexed content is more likely to appear in search results, improving the chances of attracting organic traffic. It enhances the user experience by delivering relevant and timely results.
Are There Tools that Can Help With Indexing?
Yes. Tools like All In One SEO (AIOSEO) can help ensure that your site and pages get indexed. It has features like IndexNow, an advanced robots.txt editor, and much more.
Improve Your Indexing, Boost Your Rankings
Now that you know what indexing is and why it’s important, go ahead and optimize your site for indexing by search engines. Remember, with AIOSEO, you get a lot of features and tools to help you do that.
We hope this post helped you understand what indexing is and why it’s important for your SEO. You may also want to check out other articles on our blog, like our top content optimization tools or our guide on using Crawl Cleanup to boost your SEO.
If you found this article helpful, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel. You’ll find many more helpful tutorials there. You can also follow us on X (Twitter), LinkedIn, or Facebook to stay in the loop.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. We only recommend products that we believe will add value to our readers.